Tanzania is an East African country located on the Indian Ocean. Population growth continues to progress with a fertility rate of 4.8 children per woman despite an infant mortality rate of 4.1 percent. As of 2018, Tanzania’s population was approximately 56 million.
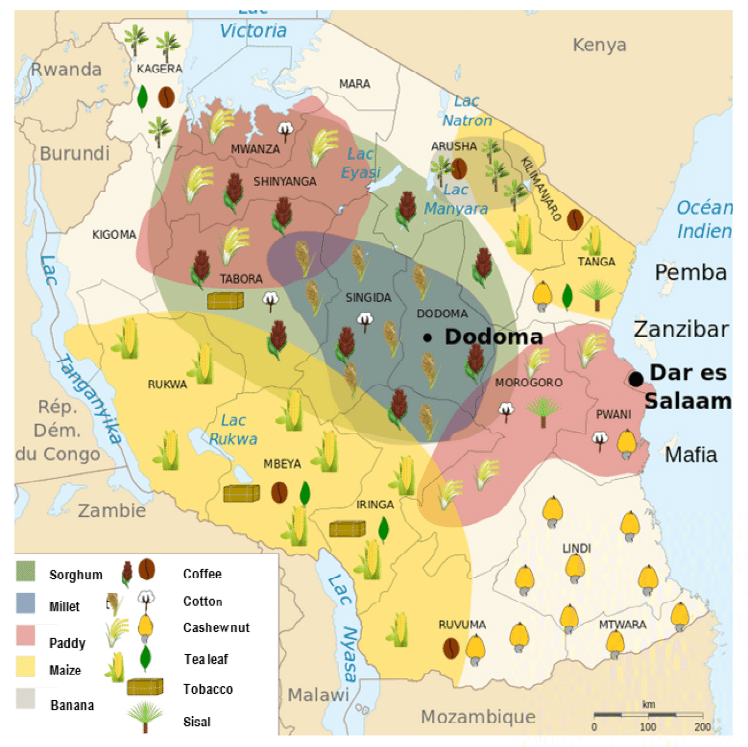
One of the poorest countries in the world, Tanzania has significant resources: the second largest gold producer in Africa, a major exporter of coffee and agricultural products, and one of the largest recipients of international aid. The weakness of the infrastructure, especially transport, and the living, sanitary and social conditions, slow down the development of the country. Conversely, access to education and literacy rates have increased since the beginning of the 21st century (87% in 2015 according to UNESCO).
The development of infrastructure, the construction of hospitals, universities, roads, the improvement of railways, the increase in mining capacity, the fight against corruption, are the main lines of work of the government with an economic growth that is increasing but remains insufficient to meet the needs of the population.